I saw berberine as part of a height stack and wanted to see if it could have any impact. Berberine is a part of many plants so it is available to the average population. So I searched if berberine had any impact on bone or cartilage.
Possible therapeutic effects of berberine on bone damage in high-fat diet-induced obese rats
“After treatment with berberine, TNF-α, IL-1β and the number of adipocytes in bone marrow were significantly decreased, and P1NP levels were higher in the HB group than in the HFD group.”<-so berberine could be used to prevent over inflammation. I don’t know if this would have any impact in healthy individuals.
“berberine chloride exerted protective effects on bone in an osteoporotic rat model induced by ovariectomy, and berberine significantly increased femur load and stiffness in glucocorticoid treated animals”
This is the study that indicates that berberine may have a positive result on longitudinal bone growth:
“Female Sprague–Dawley rats (28 days old; n = 72) were divided into six daily treatment groups: control (distilled water), Huang Bai (100 and 300 mg/kg), recombinant human GH (rhGH; 20 μg/kg), estradiol (1 μg/kg), and triptorelin (100 μg).”
“Expression of IGF-1 and BMP-2 in the hypertrophic zone was higher in all experimental groups.”
“Huang Bai promoted GH mRNA and protein in pituitary cells and inhibited GnRH mRNA expression in hypothalamus cells “
“Huang Bai contained one representative component: 24.36 mg/g berberine chloride.”<-Huang Bai contains berberine.
“Longitudinal bone growth rates of the Huang Bai 100 mg/kg, rhGH, and triptorelin groups were significantly higher than that of the control group”
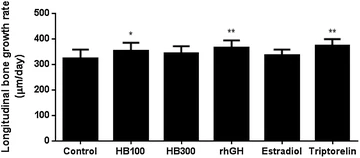
It does not look like higher doses of berberine had a benefit. It is important to note that the mice in these studies do not get as diverse a diet as a normal human so it’s possible that it would have no effect on a human.
“Huang Bai stimulates longitudinal bone growth and chondrocyte proliferation by upregulating BMP-2 and IGF-1 expression in the growth plate. However, it has no effects on pubertal onset and estrogenic activity.”
Berberine for bone regeneration: Therapeutic potential and molecular mechanisms
“Berberine promotes osteogenesis”
“the migration of BMSCs to target organs is also of great significance for repairing the damaged bone tissues. Berberine can promote this process by activating PI3K/AKT pathway”
“berberine can activate the expression of key osteogenic transcription factor Runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2) through the p38MAPKs pathway, thereby promoting bone regeneration”
“berberine was confirmed to be able to reduce the apoptosis of BMSCs and promote bone regeneration by up-regulating the expression of anti-apoptotic factor Bcl-2, down-regulating the expression of pro-apoptotic factor bax and cleaving caspase-3 in the apoptosis pathway”
“oral berberine has poor bioavailability due to the first pass effect in the intestine. Currently, there are
some solutions, such as D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS), that can increase the absorption of berberine in the intestine to improve the bioavailability”
In one study mentioned by the review “Mice treated with berberine showed better cartilage surfaces
with cracks and less cartilage degradation”
So it’s possible that berberine could be used to effect height but there’s lots of things that increase BMP-2 and IGF-1. It’d have to be studied more.
